

2 CrO42-(aq)
+ 2 H+ (aq) ![]() Cr2O72-(aq)
+ H2O (l)
Cr2O72-(aq)
+ H2O (l)
| When solid potassium chromate, K2CrO4 is dissolved in water it forms a yellow solution. When solid potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7 is dissolved in water the resulting solution is orange. The colors come from the negative ions: CrO42-(aq) and Cr2O72-(aq). However, in solution these ions are actually in equilibrium as indicated by the equation: |
|
|
2 CrO42-(aq)
+ 2 H+ (aq) |
A solution of chromate ions | A solution of dichromate ions |
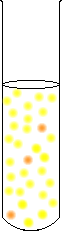 |
In a solution we call a chromate solution, there is also a little bit of dichromate, but the predominant color will be yellow. |  |
In a solution we call a dichromate solution, there is also a little bit of chromate, but the predominant color will be orange. |
| 2 CrO42-(aq) +
2 H+ (aq) |
2 CrO42-(aq)
+ 2 H+ (aq) |
||
The chemical reaction in each test tube is the same. However, the relative abundances of each ion are different, and this has been illustrated by different size letters for each species present.
What happens if we add some hydrochloric acid?
What happens if we add some sodium hydroxide?
What happens if we add some barium nitrate?
Copyright © 1998 - 2008 David
Dice